After a time-consuming, major Windows update, you may notice some of your personal files are missing. Often, recovering these files is simple—go to the Windows.old folder (created during major updates) on your C: drive and copy your data from there. However, if you chose to keep nothing during the update prompt, Windows automatically deletes the Windows.old folder after 10 days. The sections below will show you how to retrieve your files from the Windows.old folder—even if you can’t locate it in the C: drive.
What is Windows.old?
Windows.old folder is automatically created every time you switch to a new version of Windows. It will contain all files you had on the previous OS, such as system files, account settings, and installed programs. With it, you can easily restore a previous version of Windows if something goes wrong or you don’t like it.
If you can’t find it, there’s still a possibility to restore Windows.old files. This is because they are still on your PC, and space is just marked as empty. But you will have to act fast, as any new file can overwrite it, leaving you no chance of recovery. Unfortunately, if you are trying to restore files from an SSD, keep in mind that your chances of recovery are very low.
How to Restore Files from the Windows.old Folder
If it’s been less than 10 days since you updated Windows, you can locate and restore your files from the Windows.old folder using Windows Explorer.
Here’s how:
- Open Windows Explorer (Windows Key + E), and click on This PC in the sidebar.
- Navigate to C:\Windows.old\Users. You can simply copy and paste the folder path in the File Explorer address bar at the top.
- Look for your files, select and copy them to some other folder.
Unable to locate the files you were looking for? Use the Windows search feature with the C: drive open, before attempting full-fledged C: drive data recovery—click on the search bar towards the top-right corner of Windows Explorer and type in the name of the file you’re looking for.
Ways to Recover Deleted Windows.old Folder
Option A: Recovery Software
Restore Deleted Windows.old Folder via Disk Drill
Your best bet is to find a reliable data recovery app. I’ve decided to go with Disk Drill Data Recovery, as it has already proven itself in the past. It supports hundreds of popular file types, works quickly, and has a user-friendly interface. This is a premium app, but you can get a trial to try it out for free. This way, you can recover up to 500 MB of files.

Here is how you can use Disk Drill to restore deleted Windows.old files.
- Download and install Disk Drill. Ideally, install Disk Drill to an external USB drive or something similar.
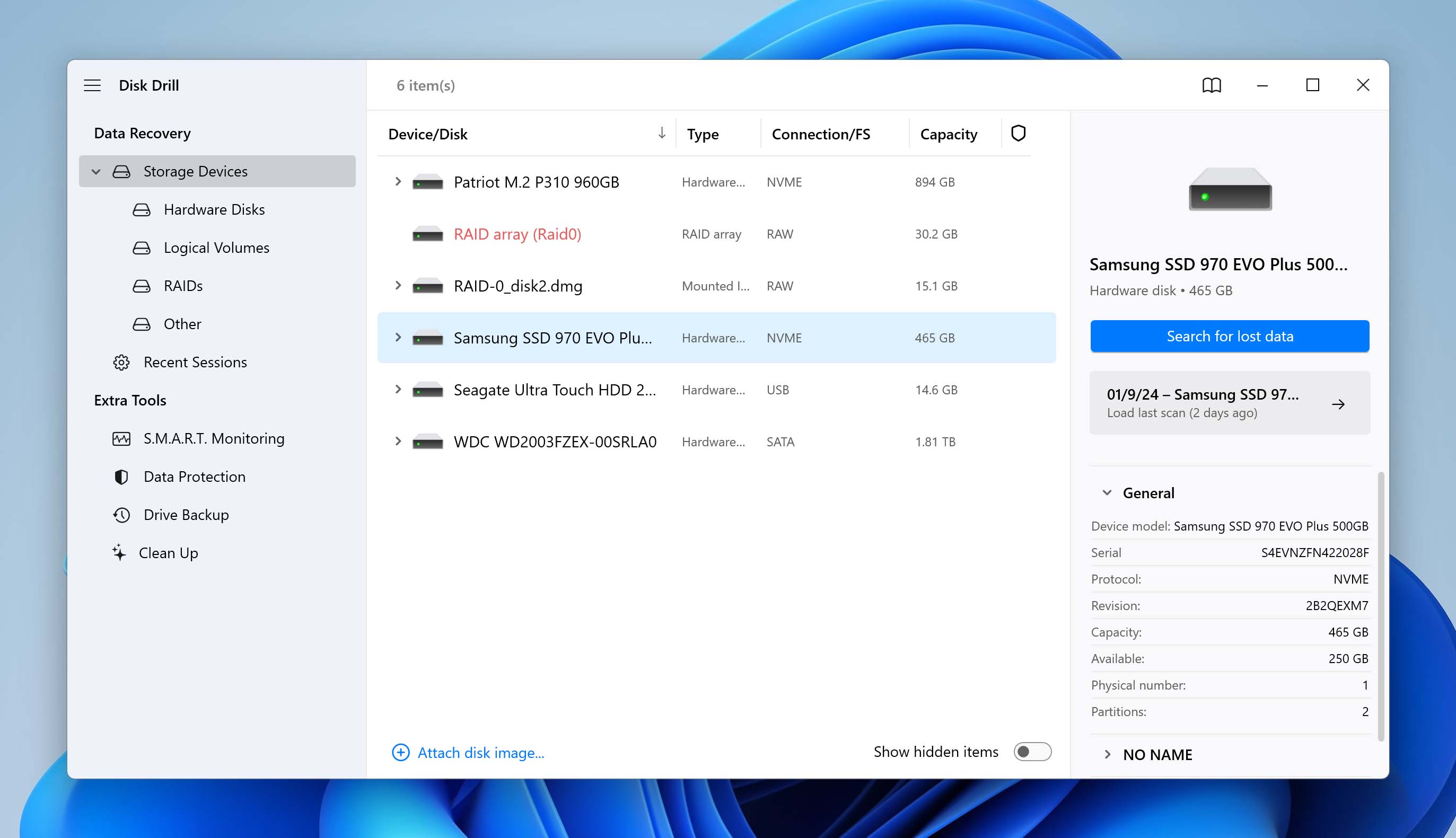
- Open Disk Drill, select your PC’s internal drive (the one which contains the C: partition), and click on Search for lost data.
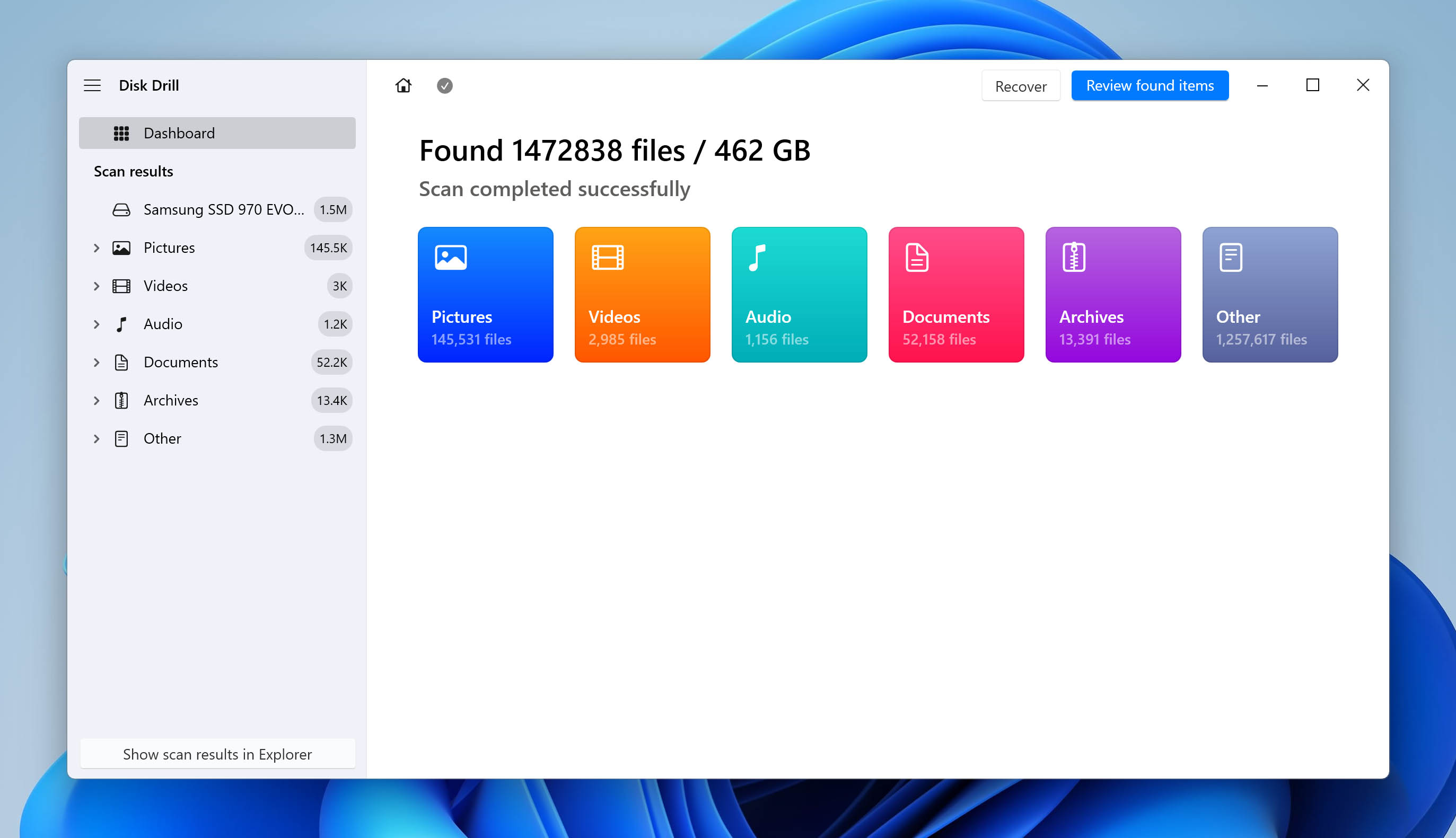
- Click Review found items to view all recoverable files. Only wish to recover a certain file type? Click on the relevant file type tile instead (Pictures, Videos, Audio, Documents, Archives, and Other).
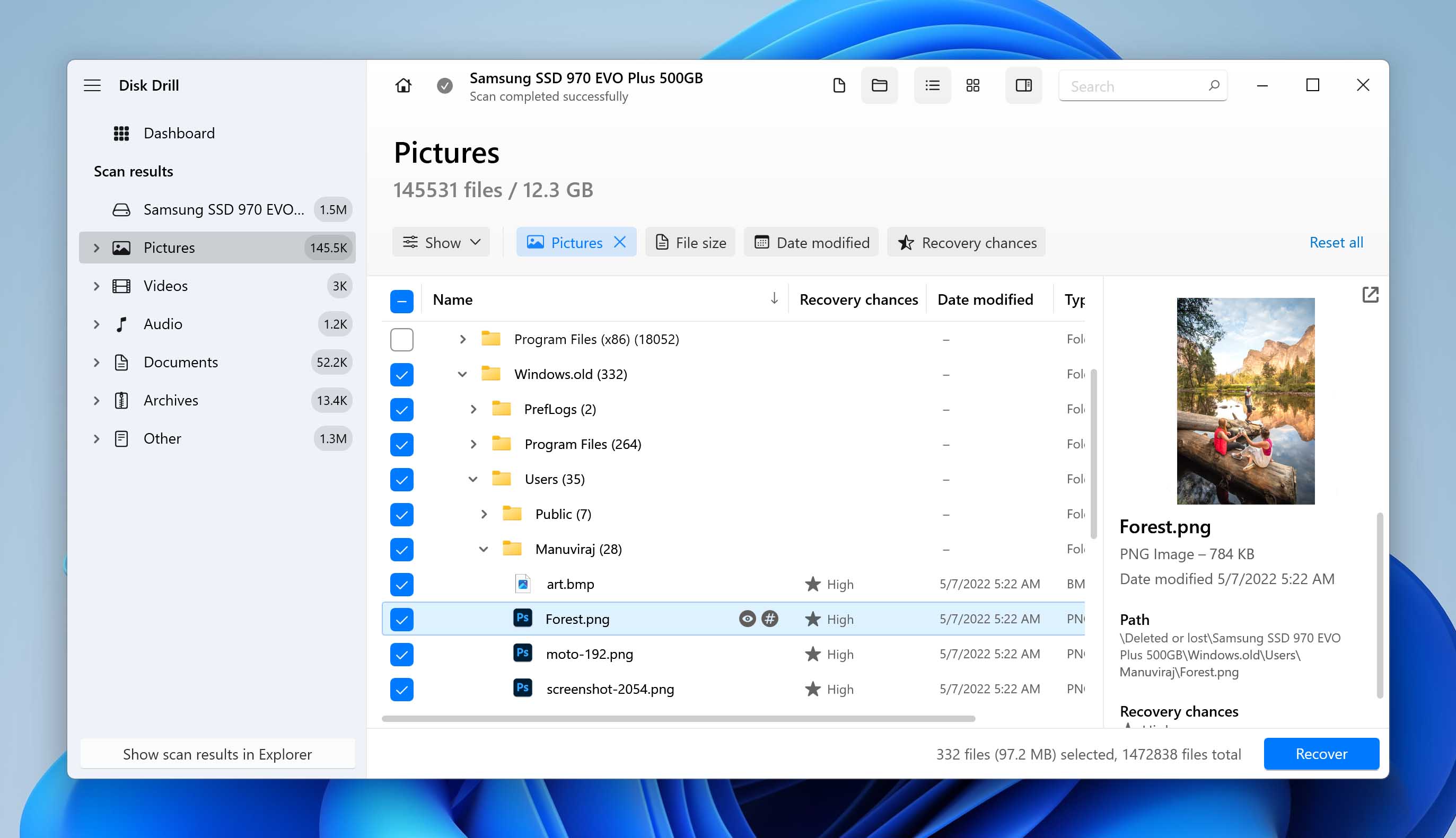
- Expand the Deleted or lost and Reconstructed sections.

- Find and expand the Windows.old folder. Select the files you wish to recover. Disk Drill displays a preview of the currently selected file, but you can manually preview any file by clicking the eye icon next to its filename. Click on Recover once you’ve confirmed your selection.
- Choose a recovery destination for the files and click Next.

- Disk Drill will recover the selected files from the Windows.old folder.
Note: Disk Drill won’t let you restore deleted Windows.old files to the same drive.
Recover Deleted Windows.old Files via EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard
Here we have another great solution for restoring Windows.old files. EaseUS has been in the data loss business for 15+ years, and as such is very versatile. It has a minimalistic interface that is easy to navigate as a casual user. Its recovery rate is very high, thanks to the support for 500+ file formats. Although it’s a bit expensive and slow, it’s also really reliable.

Note: you will have to purchase 1-month ($70), 1-year ($100), or a lifetime subscription ($150) before recovering your data.
To retrieve Windows.old with EaseUS just:
- Download and install EaseUS Data Recovery.
- Open EaseUS Data Recovery, select the C: drive, and click Search for Lost Data.

- Navigate to the Windows.old folder in the scan results screen. Use the sidebar to expand and locate it. If you only wish to see certain file types, click the Type option in the sidebar and select the required file type.

- Select the files you wish to recover. While you can’t see a full-quality preview in the EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard’s free version, you can switch the display options to Icons (thumbnails), instead of Details (list). Click Recover once you’ve confirmed your selection.
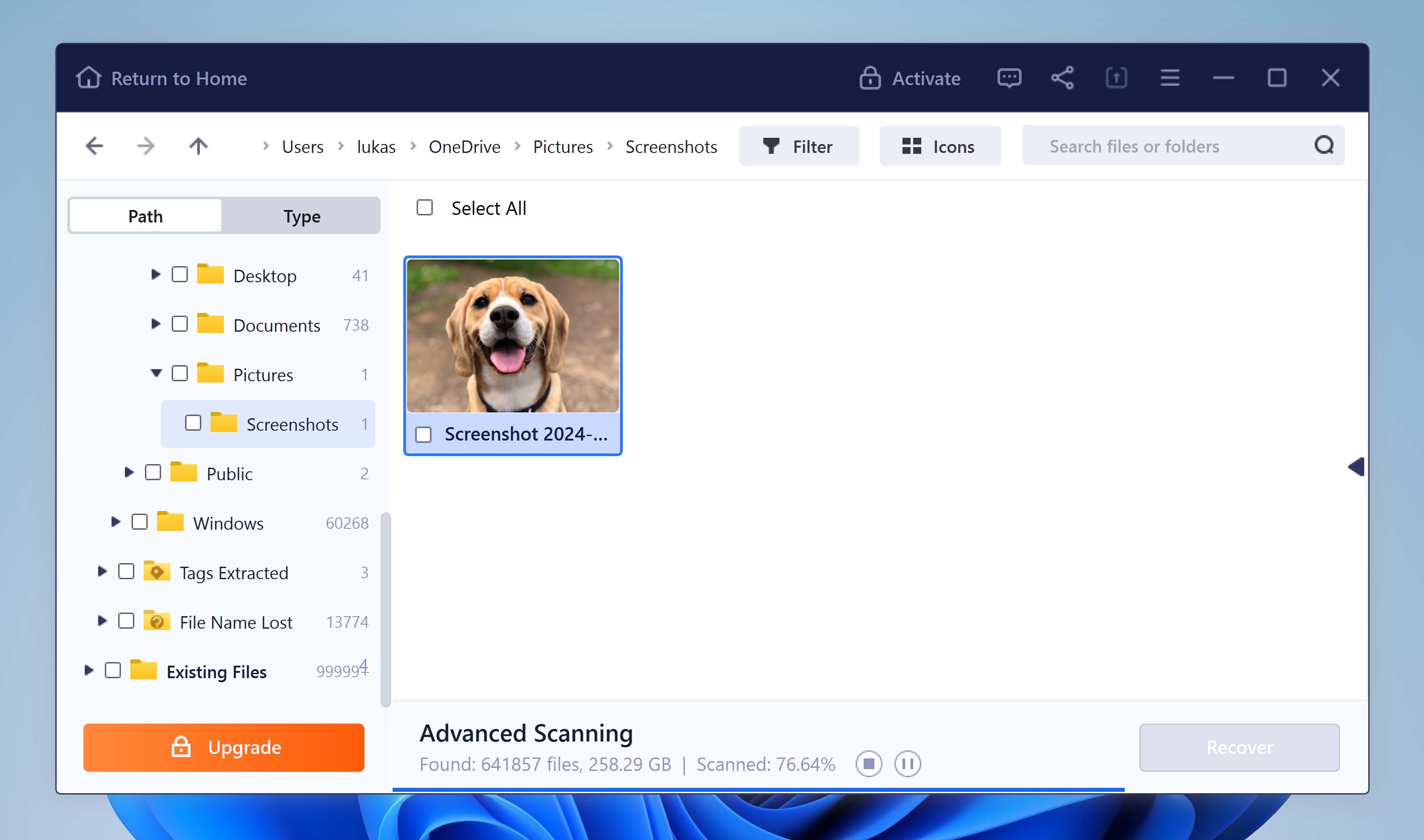
- Browse for a recovery destination and click Select Folder.
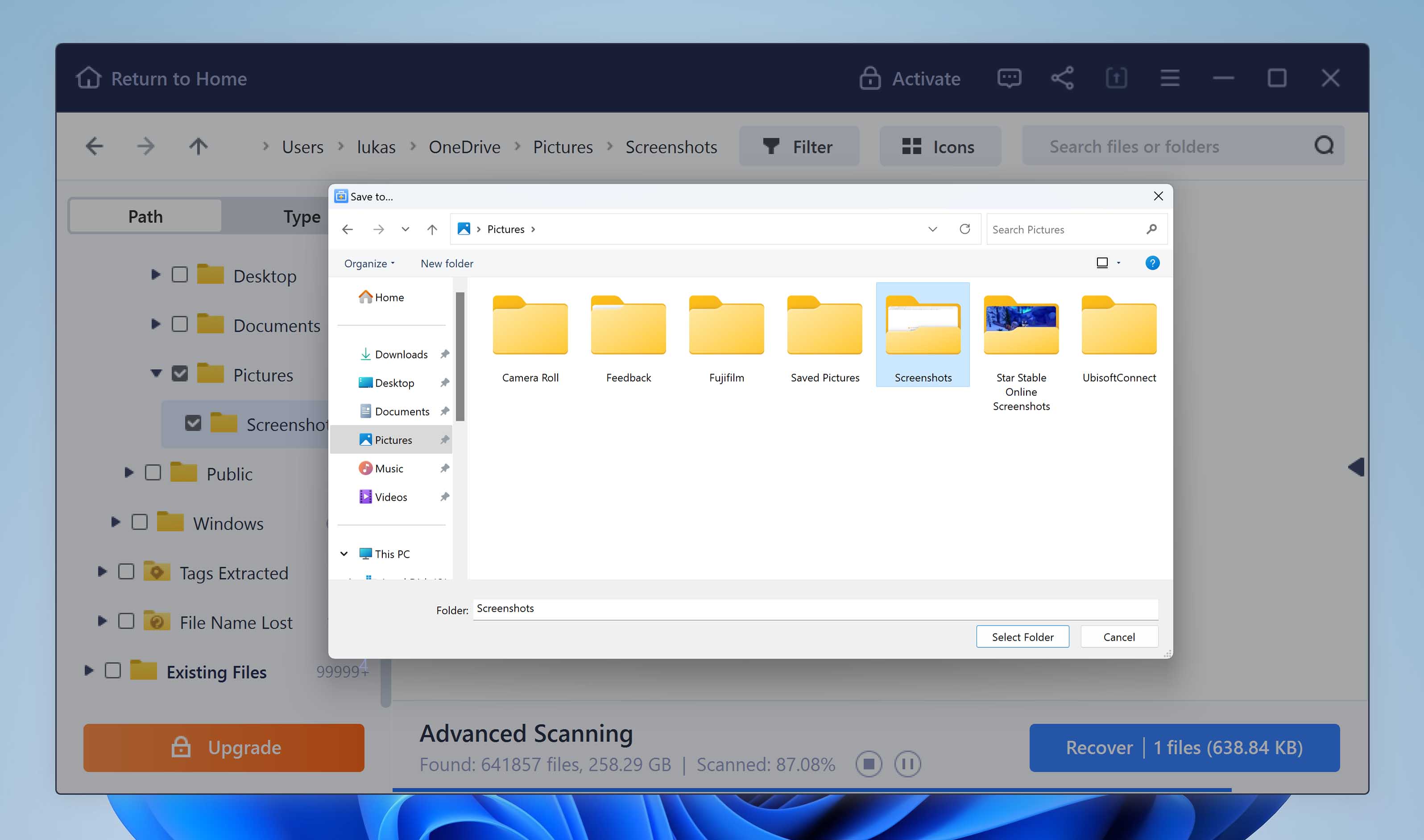
- EaseUS Data Recovery will recovery the selected files.
Recover Windows.old Folder with Windows File Recovery
If both of these apps are too expensive, you can use a native recovery tool from Microsoft. Windows File Recovery is free and powerful software that should restore specific files from Windows.old without any problems. Just follow this process.

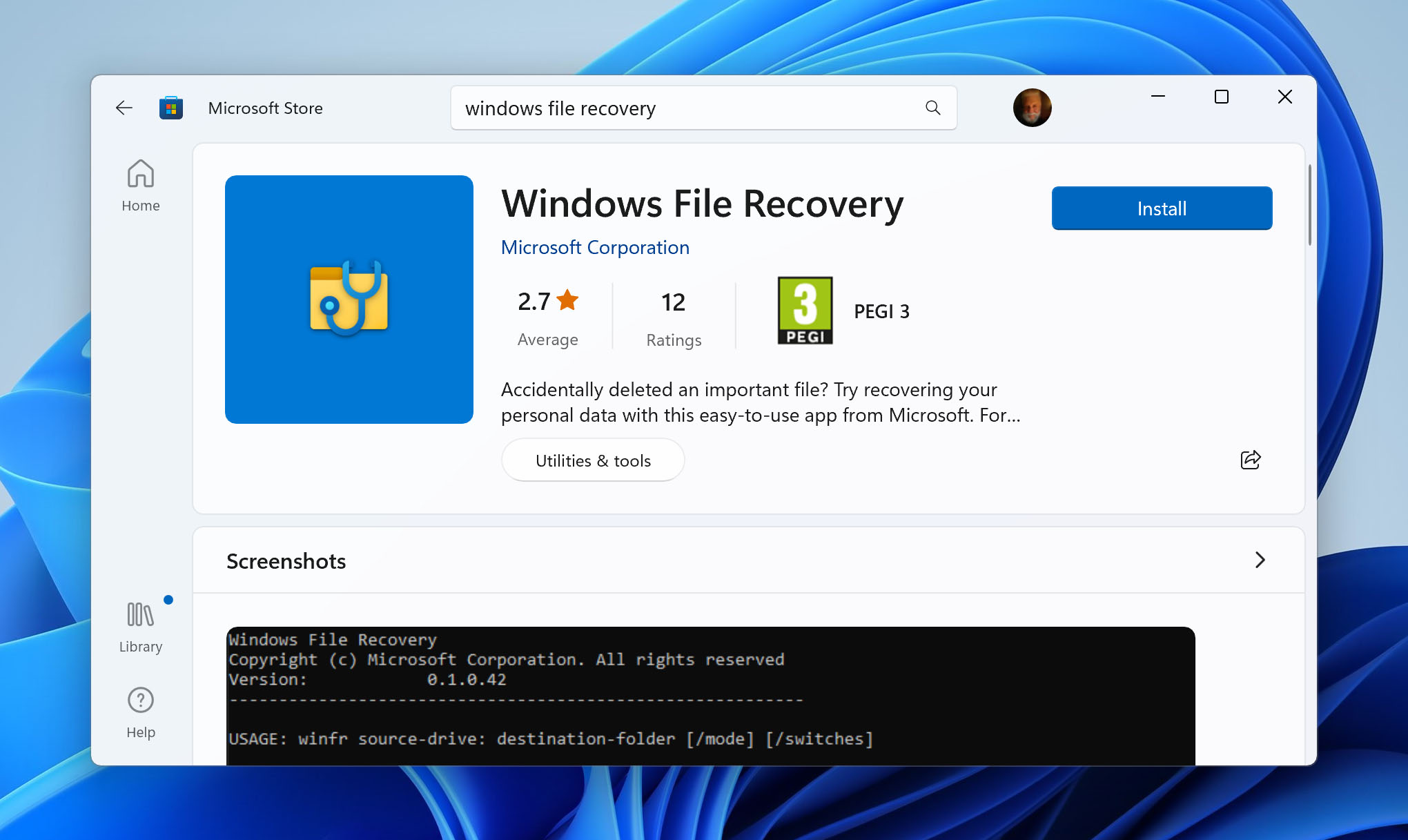
- Download Windows File Recovery from Microsoft Store.
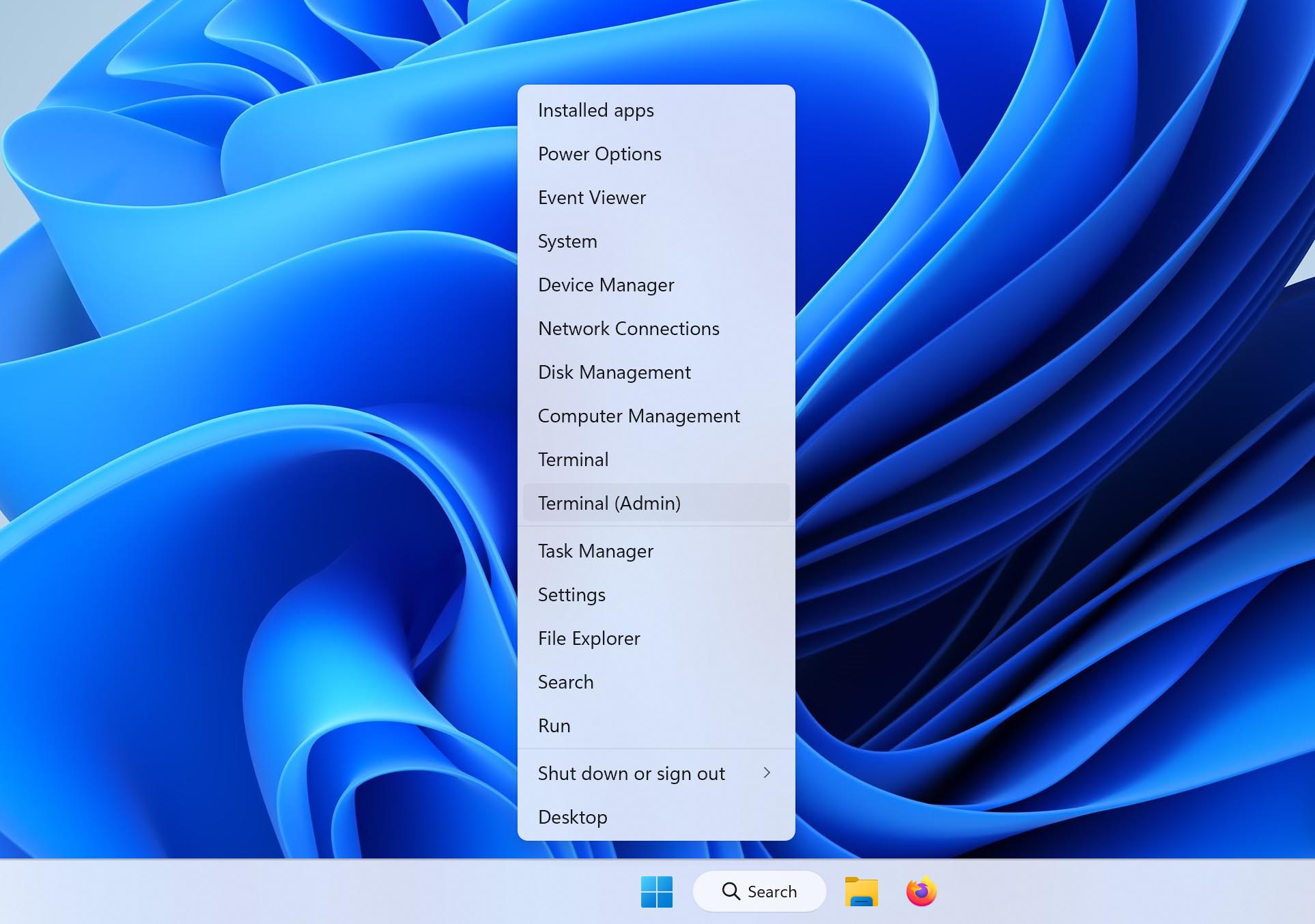
- Run Terminal. This is a command-line program that will run Windows File Recovery. Right-click on the Start menu and select Terminal (Admin).
- Choose Scanning Method. Windows Powershell lets you choose between 3 types: Segment, Default, and Signature. The Default mode is similar to a quick scan, while Segment mode lets you scan the drive thoroughly. With Signature mode, you can scan by different file types, such as MP3, JPEG, PNG, and so on. We will be focusing on the first two.
- Regular Mode. This is the standard recovery option for non-corrupted NTFS drives. Simply write the following line in the command interface: winfr C: E: /regular /n \Windows.old\Users\%Username%
- C stands for the drive that contains Windows.old folder
- E is for the drive where you wish to restore the files (could also be D:, F:, etc.)
- n lets you filter your search by providing a file path
- /regular activates standard recovery
Next, click enter and accept the command by typing y, which will initiate the scan.
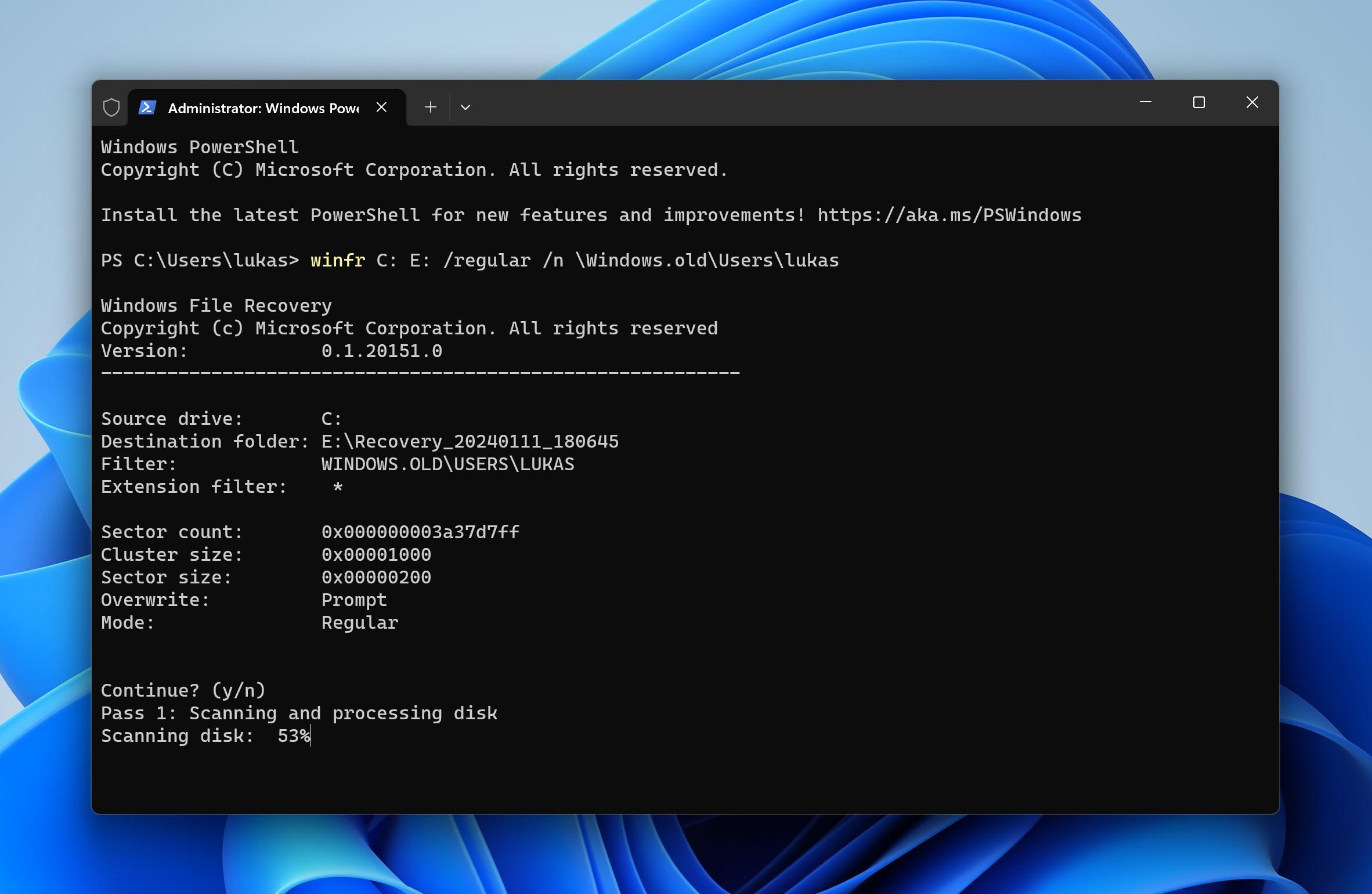
After the scan is done, recovered files will be available on the drive that you previously chose.
- Regular Mode. This is the standard recovery option for non-corrupted NTFS drives. Simply write the following line in the command interface: winfr C: E: /regular /n \Windows.old\Users\%Username%
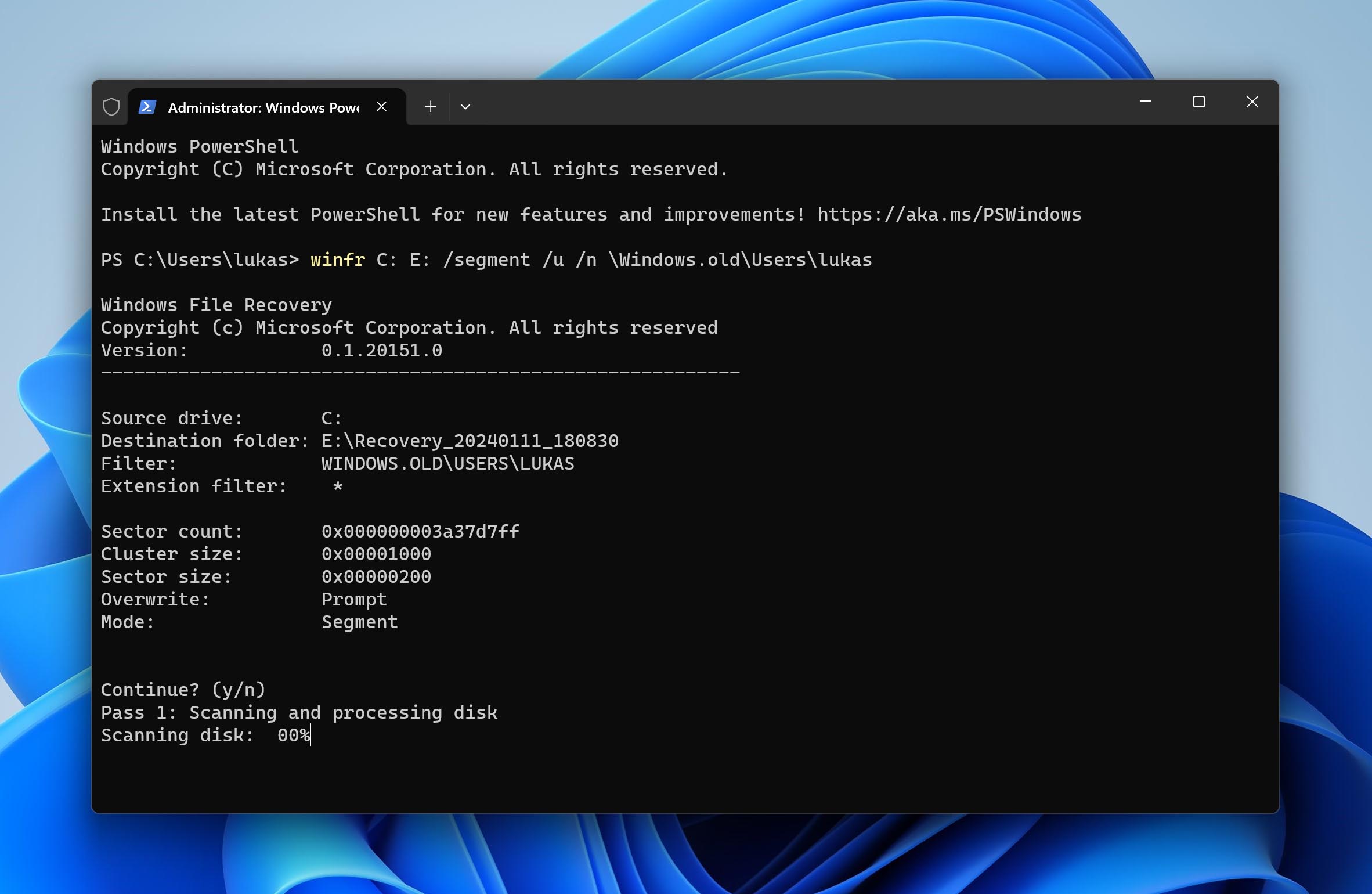
- Segment Mode. Segment mode is a more thorough method, but the process is nearly identical. You’ll just need to make a small change to the line in the Powershell, so that it looks like this: winfr C: E: /segment /u /n \Windows.old\Users\%Username%
- /u will restore undeleted files from a location such as Recycle Bin
- /segment is a recovery option that uses file record segments
Option B: System Restore
Alternatively, you can use a backup feature that creates “snapshots” of the current state of your PC. These are called restoration points. You can create them manually, or automatically.
To recover Windows.old with System Restore, you’ll just have to.
- Open Start.
- Type “Restore” and click on the top result.

- Select System Restore.
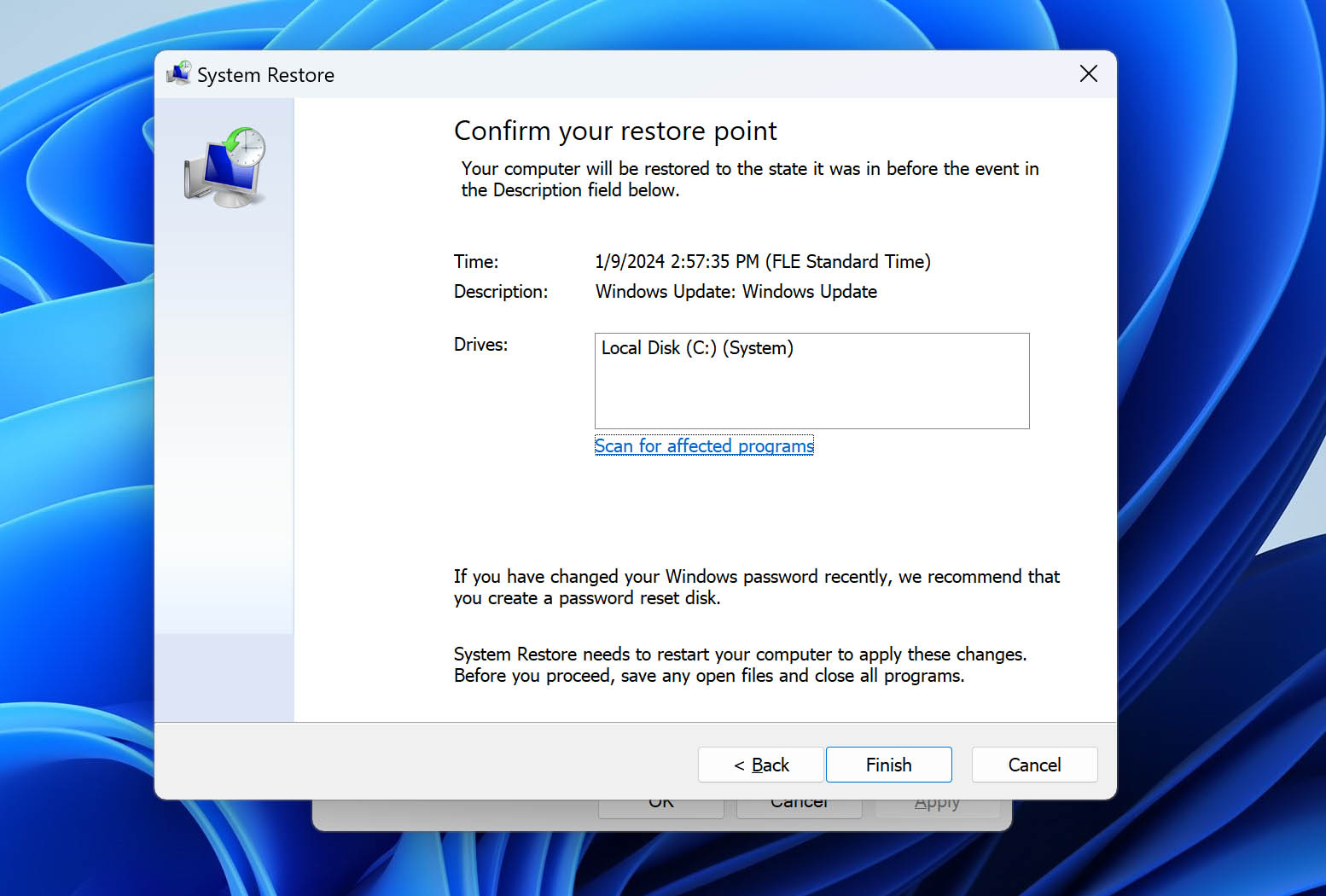
- Choose your Restore Point. A wizard will throw in a recommendation, but you can also select other backups if available. Just make sure that they are within the first 30 days. On the next screen, you can Scan for affected programs to see which apps will be removed if you proceed.
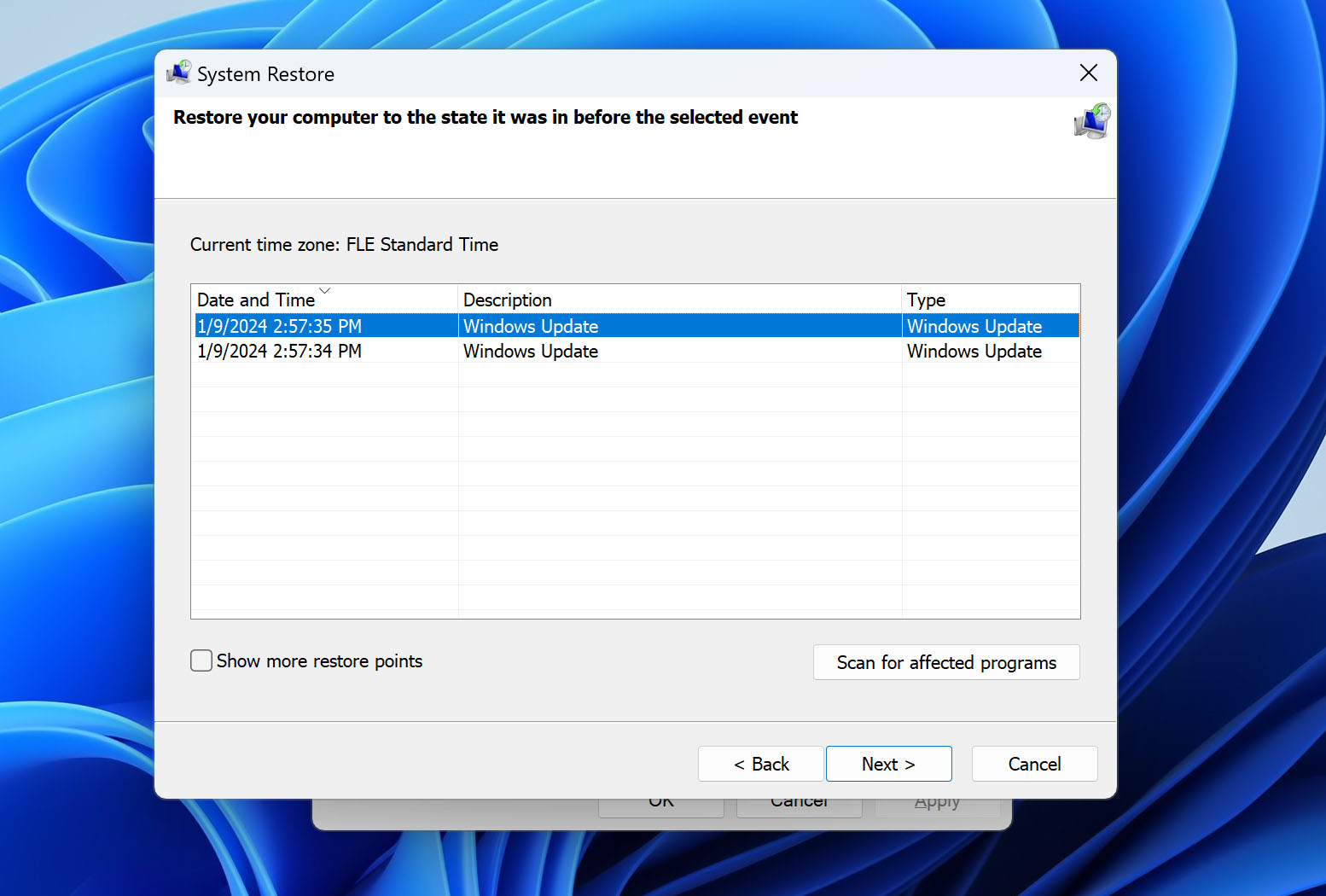
- Click Next and Finish to revert your PC to the previous restore point.
Where to Put Files from the Windows.old Folder
For better file management, put the copied files from the Windows.old folder to the respective user library folders (Pictures, Documents, etc.) located in C:\Users\<username>. Use an external storage drive if the file sizes are huge, and you wish to free up that space on your C: drive.
Try to only copy important standalone files like photos, documents, videos, and music. It’s futile to copy any programs and system files from the Windows.old folder, as they won’t work with the new installation.
If you wish to recover stuff like save games and temporary files, first familiarize yourself with where the respective files are stored by default. For example, many video games store save games in the C:\Users\AppData… directory. Use the internet or the developer’s website to find out where the relevant files are stored, find the corresponding files within Windows.old, and copy the files to the correct folder in your current Windows installation.
Often, files and folders from the Windows.old folder has separate permissions. To access and modify these files, adjust the permission settings accordingly.
FAQ
Can you recover Windows.old files?
Yes. To do this, go to Local Disk (C:) > Windows.old > Users > * User*, and copy the files that you wish to restore to another folder.
Where are old Windows files stored?
They are located on the drive where your Windows is installed. Usually, this is a C: drive.
Can you recover the deleted Windows.old folder?
This might be possible by utilizing good recovery software such as Disk Drill, Windows File Recovery, or Ease US. You can also use System Restore if you’ve set up restore points in the first 10 days.
Parting Words
As you can see, it’s fairly easy to move files from the Windows.old folder to keep them permanently. Even if there is no Windows.old folder, there are numerous methods you can use to solve this problem. You’ll just have to act quickly to get the highest chance of recovery.
This article was written by Marko Medakovic, a Author at Handy Recovery Advisor. It was recently updated by Manuviraj Godara. It was also verified for technical accuracy by Andrey Vasilyev, our editorial advisor.
Curious about our content creation process? Take a look at our Editor Guidelines.
