While RAID 10 offers robust protection against drive failures, accidental file deletions and corruptions or failures can still occur, leading to loss of data. But don’t lose hope; by using good data recovery software, successful recovery of your lost data is possible.
You’ll need a good RAID 10 data recovery program to restore deleted files and undo your data loss. This guide will explore the best methods to restore deleted files from your RAID 10 Drives.
RAID 10 Explained
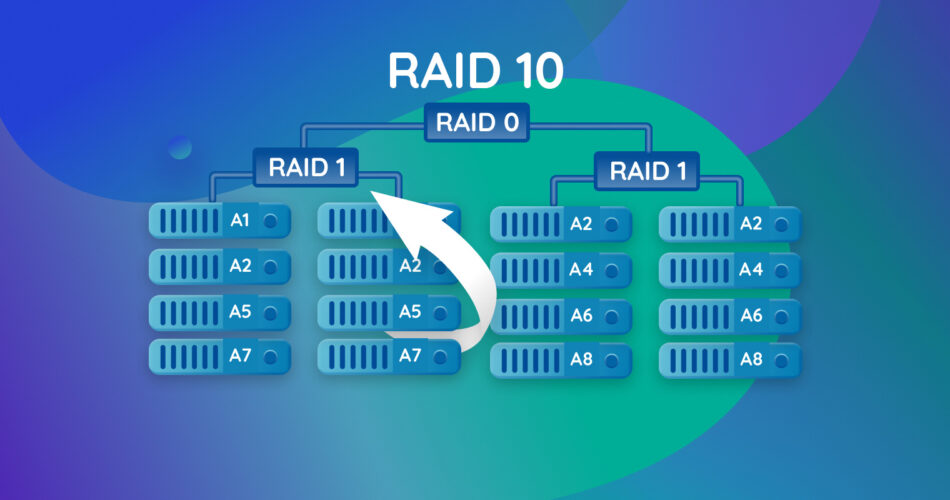
RAID 10 (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), also known as RAID 1+0, is a method of combining multiple hard drives to create a more reliable and faster storage system for your data. It is a nested or hybrid RAID, which is a combination of two RAID levels: RAID 1 and RAID 0.
This combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0 ensures mirroring for data redundancy and striping for performance. It requires at least four drives, where data is mirrored across two pairs of drives, and then the mirrored pairs are striped to boost speed and protect your drives against failures.
RAID 10 provides better throughput and latency than all other RAID levels and has decent security capabilities too. Here are some advantages and disadvantages explained in simple terms:
✅ Advantages:
- Data Redundancy: RAID10 uses mirroring (RAID1) to create an exact duplicate of your data on multiple drives in real-time. This redundancy ensures that if one drive fails, your data is still safe on the other drive. Thus by using RAID 1, RAID 10 helps protect your system against hardware failures.
- Fast Rebuild Times: In the event of a drive failure, the RAID10 array can rebuild itself quickly by copying the data from the surviving mirrored drive. As such, compared to other RAID configurations, the window of vulnerability to data loss is relatively smaller.
- Fast data recovery: A RAID 10 array recovers data quickly and with little downtime because it does not rely on parity to recreate any data lost due to drive failure.
- Improved performance: RAID10 uses striping (RAID0) to spread data across multiple drives, which can result in faster read and write speeds. This improved performance can be beneficial in scenarios that require real-time data access or high-performance computing.
- Features best traits of both RAID 1 and RAID 0: By combining both RAID methods, RAID 10 provides both the speed advantages of RAID 0 and the data redundancy of RAID 1 for improved fault tolerance and data protection.
❌ Disadvantages:
- High costs: RAID10 requires a minimum of four drives since it combines both mirroring and striping techniques. As a result, it can be more expensive to implement compared to other RAID configurations that use fewer drives.
- Limited data protection: RAID arrays are not a substitute for regular data backups. While it protects against certain hardware failures, it does not safeguard against data corruption, accidental deletions, malware, or physical damage to your drive.
- Limited usable capacity: In RAID10, only half of the total drive capacity can be used for data storage. For example, in a four-drive RAID10 setup, if each drive is 1TB, the usable capacity will be 2TB because the remaining 2TB will be used for mirroring and data redundancy.
- Limited scalability: Expanding RAID10 can be difficult and expensive. To increase storage capacity, you need to add more mirrored pairs, which require additional drives and may need a complete array rebuild.
Is it Possible to Recover Data From RAID 10 With Failed Drives?
Yes, it is possible to recover data from a RAID 10 array with failed drives, but the success of the recovery process depends on how many drives failed. RAID 10 offers some level of data redundancy, which means that as long as at least one drive from each mirrored pair is functional, there is a chance to recover the data.
To recover files from a RAID 10 array, you must first identify the drives that have failed in the RAID 10 setup using management interfaces or software provided by the RAID controller. After replacing the failed drives with new compatible ones, the RAID 10 array will automatically start the rebuilding process. Data from the surviving mirrored drives is copied to the new drives to restore data redundancy. The time required for this RAID rebuild depends on the drive sizes and data amount, and the array may experience reduced performance during this process.
If multiple drives from the same mirrored pair fail or issues arise during the rebuild, you should consider contacting a data recovery service. However, it’s important to remember that RAID is not a substitute for regular backups, and maintaining regular backups of critical data remains crucial for securing your data.
How to Retrieve Deleted Files from RAID 10 Array
In the case of a RAID 10 drive failure, you can employ the use of hard drive data recovery software compatible with RAID configurations. Good RAID 10 recovery software like Disk Drill is even capable of recovering data from corrupted drives.
In the case of NAS (Network Attached Storage) data recovery, your devices must be connected to the system directly and recognized as data storage. Otherwise, the hard drives must be unmounted from the NAS and connected to the PC for scanning by Disk Drill.
Disk Drill supports RAID 10 (RAID 1+0) level data recovery and supports most popular file systems, including FAT16/FAT32/exFAT, NTFS, NTFS5, HFS, HFS+, APFS, ext2/3/4 and RAW drives. Here is a complete Disk Drill review.
As long as your RAID 10 array is detected by Disk Drill, even if it’s corrupted, it can be scanned, and your files can be recovered. Here’s a step-by-step guide for RAID 10 array data recovery using Disk Drill:
- Download and install Disk Drill.
- Open Disk Drill, click on RAIDs under the Storage Devices tab and select your RAID 10 array. It’s important to scan the entire RAID array rather than individual member drives to ensure successful scan results. Now click on Search for lost data.

- Once the scan is complete, click on Review found items to see all the recoverable data. You can filter for specific file types using Disk Drill’s intuitive GUI.

- Check under the Deleted or lost and Reconstructed sections to view deleted files from your RAID 10 array. Or expand the Existing section to view files currently present on your drive.

- Preview and select your files, choose a recovery destination, then click Recover. Up to 500 MB of data will now be recovered under Disk Drill’s free trial.

FAQ
Does RAID 10 count as backup?
No, RAID 10 is not equivalent to a data backup. If data corruption is caused due to your operating system or external software rather than internal drive corruption, the corrupted data is sent to both drives simultaneously. So even though RAID 10 writes data to two disks simultaneously, it does not count as a data backup.
What is the disadvantage of RAID 10?
RAID 10 drives have limited scalability and only make commercial sense at smaller-scale integrations. And while they help protect against data loss through hardware failures, they aren’t a substitute for backups. Another drawback of RAID 10 is that due to mirroring, only 50% of the storage capacity is actually usable.
What happens when RAID 10 drive fails?
If a single drive in a mirrored pair of RAID 10 drives fails, its twin will still hold functional data due to data redundancy. However, a standard four-disk RAID 10 array can only protect against one drive failure in each mirrored pair of disk drives. If multiple drives fail, total data loss occurs.
How to recover files from RAID 10 Array?
Here are simple step-by-step instructions to recover data from RAID 10 arrays:
- Download and install Disk Drill.
- Connect your RAID 10 set or individual drives to your system.
- Select the drive and click “Search for lost data”.
- Scan, preview, and select recoverable files.
- Click Recover and select a recovery folder.
Conclusion
RAID 10 drives can prove to be useful tools for increasing fault tolerance and offer better data protection than regular drives. Being a combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0, these hybrid drives provide both redundancy and performance benefits, making them a popular data storage solution. However, despite these advantages, RAID 10 is not immune to data loss events like human errors, software issues, or corruption.
The first and foremost priority when dealing with data loss on RAID 10 is to immediately stop any further writes to the array to prevent data from being overwritten and to improve the chances of a successful recovery.
Using competent software like Disk Drill, you can perform an at-home RAID 10 data recovery, even for corrupted drives. Furthermore, it is important to understand that RAID 10 drives are not a substitute for backups. It’s important to have a comprehensive and up-to-date backup strategy for all your important files.
And if all else fails, you can consider taking your RAID 10 drive to a professional data recovery service for the best chances of recovery.
This article was written by Vihaan Jain, a Staff Writer at Handy Recovery Advisor. It was also verified for technical accuracy by Andrey Vasilyev, our editorial advisor.
Curious about our content creation process? Take a look at our Editor Guidelines.